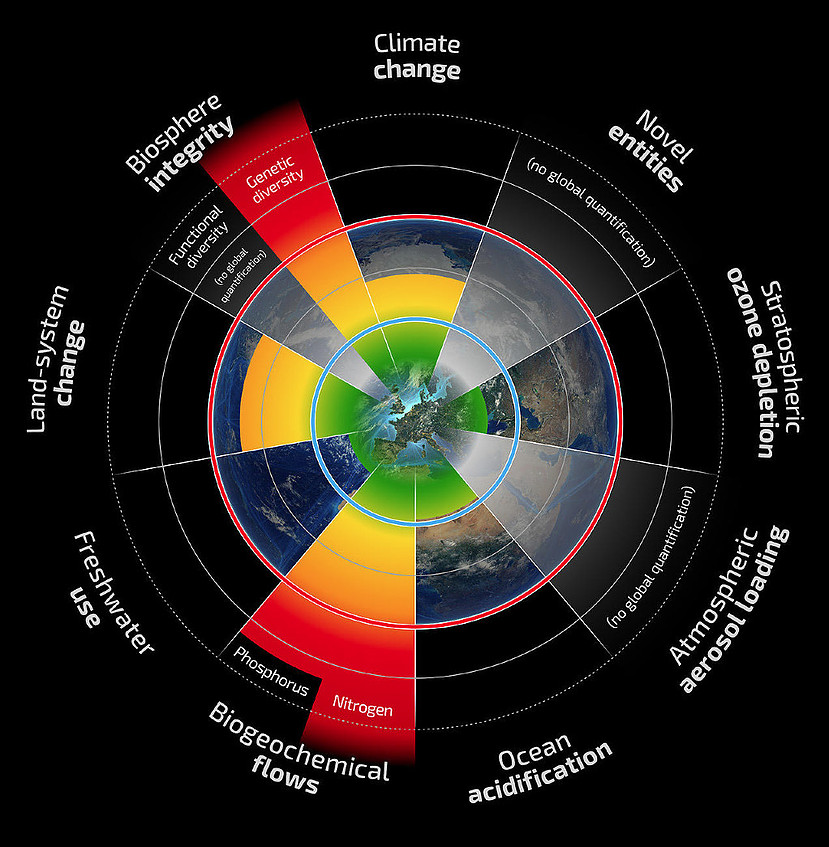
The concept of “Planetary Boundaries” was introduced in environmental science to describe the limits within which humanity can safely operate to maintain a stable and hospitable planet. These boundaries represent key Earth system processes and are defined to help us understand the environmental limits beyond which human activities could lead to irreversible and potentially catastrophic changes in the Earth’s natural systems. The concept was proposed by scientists Johan Rockström and Will Steffen in 2009. To learn more about the status of the 9 Planetary Boundaries Watch This Video and read this Scientific American Article.
The Nine Planetary Boundaries are:
- Climate Change: This boundary pertains to the concentration of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere, primarily carbon dioxide (CO2). The goal is to limit global temperature rise to avoid dangerous climate change.
- Biodiversity Loss: This boundary is related to the rate of extinction of species and the loss of biodiversity. It aims to prevent the destruction of ecosystems and the extinction of species.
- Nitrogen Cycle: This boundary focuses on the human-driven disruption of the nitrogen cycle, particularly excessive nitrogen pollution from fertilizers and other sources.
- Phosphorus Cycle: This boundary relates to the disruption of the phosphorus cycle, primarily due to the excessive use of phosphorus in agriculture and its release into the environment.
- Land Use Change: This boundary addresses the transformation of natural landscapes into urban areas, agriculture, and other human activities, leading to habitat destruction and ecosystem disruption.
- Freshwater Use: This boundary concerns the excessive withdrawal and use of freshwater resources, which can lead to the depletion of aquifers and degradation of freshwater ecosystems.
- Ocean Acidification: This boundary is related to the increasing acidity of the oceans due to the absorption of excess atmospheric CO2, which can harm marine ecosystems.
- Atmospheric Aerosols: This boundary deals with the release of certain pollutants into the atmosphere, like black carbon and sulfate aerosols, which can affect climate and air quality.
- Chemical Pollution: This boundary addresses the release of synthetic chemicals and pollutants into the environment, including pesticides, plastics, and other contaminants.
When it is said that “Humans Have Crossed 6 of 9 Planetary Boundaries,” it means that human activities have exceeded the safe limits or boundaries for six of these critical Earth system processes. Crossing these boundaries indicates that we are putting significant pressure on the planet’s ecosystems and potentially pushing them towards states that could be detrimental to both the environment and human civilization. This underscores the importance of taking urgent and effective actions to address these issues, reduce environmental impacts, and work towards sustainability.

Jeff is founder of Terra Vida Academy and has been actively involved in protecting nature for over 35 years.